List
Story > NEWS > Detail
News] Shared Economy and Social Enterprise
The implications of sharing in a shared economy are interpreted in many ways.
In a shared economy, however, the meaning of sharing has the same meaning as a common good, unlike the ownership concept of a traditional capitalist system. Sharing is a concept that encompasses all wealth-related assets, ranging from clean air to wildlife protection and judicial systems to the Internet. A shared economy is being realized through a shared-based society. A shared-based society refers to changing policies and values away from the market-oriented system that has dominated modern society for the past 200 years. A shared-based society also emphasizes the protection of private property and competitive environment from an economic perspective, democratic participation and social justice. Social enterprises based on the social economy have also come under renewed attention along with the crisis of welfare states, including economic adjustment, mass unemployment and increased poverty. The social economy has also emerged in a completely new form and content, but has been used as a strategic alternative to prescribe the expansion of social exclusion, such as mass unemployment and poverty, created by neo-liberalistic lines that have relied on the state and the market. In other words, shared economy and social enterprise have common characteristics of pursuing a social and economic system that values common values such as ideology of equality, responsibility, and value-judgment discourse to overcome problems arising from market-oriented systems such as private ownership, freedom of economic activity, and pursuit of private interests in the past. Shared economy and social enterprise emphasize that the social system and system must be changed to enable co-operational exploration, common value and equal participation, which can be called the basic principle of communalism.
First, shared economy and social enterprise regard cooperation as an important value. The shared economy is taking an equal-tier production method through cooperation. Equivalence layer production originally derives from equivalent layer communication (peer-to-peer) and means the performance of collective action by the network. That is, human social power, not mechanical power, produces results. This is because the production of the equivalence layer uses self-organization through the organization of the horizontal structure, not the way wealth is created by the hierarchical structure. The co-production of these equivalents is a more active form of cooperation in that it increases the likelihood of friction between individuals and groups. As an extended concept of social enterprise, co-operatives are the result of collective drive, including those who engage in economic activities through cooperative actions and who share a distinct purpose.

Second, shared economy and social enterprise are pursuing common values. The frame of a shared economy is based, among other things, on the 'reasonable' logic of seeking profits within a community with others, within a larger logic that values all members of the community working as achievement-oriented people. Social enterprises also have a clear purpose for the benefit of the community. One of the main purposes of social enterprise is to serve and dedicate to the community or to a particular group of people. In the same light, the characteristic of social enterprises is that they aspire to promote a sense of social responsibility at the local level. Also, the idea that social enterprises enjoy the basic rights of 'any person' as human beings is based on the principle of common good

Third, shared economy and social enterprise consider equal participation as an important factor. The emphasis on equality is evident within a shared economy. By sharing their interests, businessmen regard themselves as people who help create a fairer society. These days, people with similar interests often converge to share intangible assets such as time and space, technology and money. This common life style requires high confidence in a shared economy. In a shared economy, exchange and sharing are focused not on products but on human-to-human interaction. Social enterprises also emphasize the equality of members and the nature of participation. Social enterprises have decision-making rights that are not based on capital ownership, and the influence and management participation in decision-making by the representation and participation of users, consumers and stakeholders are important characteristics of social enterprises. Those who are determined to participate in cooperation according to the principle of equivalence have the conviction that the cooperative enterprises to which they belong will treat all members equally.
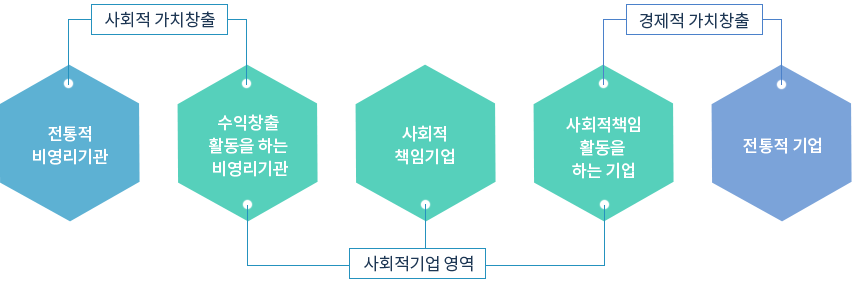
Fourth, shared economy and social enterprise mainly utilize network. The shared economy is an evolving form of traditional equal-tier production, utilizing the Internet and social networking services. That is, what characterizes a shared economy is that it maximizes the effectiveness of the network by building a platform on the Internet. Social enterprises are also the main means of corporate activity. Here, networks mean networks as social capital in social enterprise members and communities. In other words, social enterprises do not emphasize internet networks, although networks are an important means.
We looked at the similarities between social enterprises and the shared economy. As there are similar aspects, we also imagine the revitalization of a shared economy in the social enterprise sector in the future, taking advantage of the possibility of mutual cooperation and collaboration.
The implications of sharing in a shared economy are interpreted in many ways.
In a shared economy, however, the meaning of sharing has the same meaning as a common good, unlike the ownership concept of a traditional capitalist system. Sharing is a concept that encompasses all wealth-related assets, ranging from clean air to wildlife protection and judicial systems to the Internet. A shared economy is being realized through a shared-based society. A shared-based society refers to changing policies and values away from the market-oriented system that has dominated modern society for the past 200 years. A shared-based society also emphasizes the protection of private property and competitive environment from an economic perspective, democratic participation and social justice. Social enterprises based on the social economy have also come under renewed attention along with the crisis of welfare states, including economic adjustment, mass unemployment and increased poverty. The social economy has also emerged in a completely new form and content, but has been used as a strategic alternative to prescribe the expansion of social exclusion, such as mass unemployment and poverty, created by neo-liberalistic lines that have relied on the state and the market. In other words, shared economy and social enterprise have common characteristics of pursuing a social and economic system that values common values such as ideology of equality, responsibility, and value-judgment discourse to overcome problems arising from market-oriented systems such as private ownership, freedom of economic activity, and pursuit of private interests in the past. Shared economy and social enterprise emphasize that the social system and system must be changed to enable co-operational exploration, common value and equal participation, which can be called the basic principle of communalism.
First, shared economy and social enterprise regard cooperation as an important value. The shared economy is taking an equal-tier production method through cooperation. Equivalence layer production originally derives from equivalent layer communication (peer-to-peer) and means the performance of collective action by the network. That is, human social power, not mechanical power, produces results. This is because the production of the equivalence layer uses self-organization through the organization of the horizontal structure, not the way wealth is created by the hierarchical structure. The co-production of these equivalents is a more active form of cooperation in that it increases the likelihood of friction between individuals and groups. As an extended concept of social enterprise, co-operatives are the result of collective drive, including those who engage in economic activities through cooperative actions and who share a distinct purpose.

Second, shared economy and social enterprise are pursuing common values. The frame of a shared economy is based, among other things, on the 'reasonable' logic of seeking profits within a community with others, within a larger logic that values all members of the community working as achievement-oriented people. Social enterprises also have a clear purpose for the benefit of the community. One of the main purposes of social enterprise is to serve and dedicate to the community or to a particular group of people. In the same light, the characteristic of social enterprises is that they aspire to promote a sense of social responsibility at the local level. Also, the idea that social enterprises enjoy the basic rights of 'any person' as human beings is based on the principle of common good

Third, shared economy and social enterprise consider equal participation as an important factor. The emphasis on equality is evident within a shared economy. By sharing their interests, businessmen regard themselves as people who help create a fairer society. These days, people with similar interests often converge to share intangible assets such as time and space, technology and money. This common life style requires high confidence in a shared economy. In a shared economy, exchange and sharing are focused not on products but on human-to-human interaction. Social enterprises also emphasize the equality of members and the nature of participation. Social enterprises have decision-making rights that are not based on capital ownership, and the influence and management participation in decision-making by the representation and participation of users, consumers and stakeholders are important characteristics of social enterprises. Those who are determined to participate in cooperation according to the principle of equivalence have the conviction that the cooperative enterprises to which they belong will treat all members equally.

Fourth, shared economy and social enterprise mainly utilize network. The shared economy is an evolving form of traditional equal-tier production, utilizing the Internet and social networking services. That is, what characterizes a shared economy is that it maximizes the effectiveness of the network by building a platform on the Internet. Social enterprises are also the main means of corporate activity. Here, networks mean networks as social capital in social enterprise members and communities. In other words, social enterprises do not emphasize internet networks, although networks are an important means.
We looked at the similarities between social enterprises and the shared economy. As there are similar aspects, we also imagine the revitalization of a shared economy in the social enterprise sector in the future, taking advantage of the possibility of mutual cooperation and collaboration.